📌 Key Takeaways
The Timing of Termination Can Be Telling:
When an employee is terminated shortly after disclosing a qualifying medical condition or requesting accommodations, this timing may suggest a causal connection relevant under California’s Fair Employment and Housing Act (FEHA).
Employer Refusal to Engage in the Interactive Process Could Reflect Non-Compliance:
An employer’s failure to discuss or explore reasonable accommodations after receiving medical documentation may not meet FEHA procedural obligations and could indicate statutory exposure.
Patterns of Unequal or Retaliatory Conduct May Warrant Further Review:
Disciplinary action, workload changes, or denial of flexibility following a medical disclosure may help establish a pattern inconsistent with legal protections, especially when supported by documentation.
Qualified Legal Review Is Essential in Medical Termination Cases:
Statutory protections vary based on individual facts, medical condition, and documentation. Consulting with a California employment attorney is essential when wrongful termination is suspected.
The article offers an overview of potential statutory violation indicators tied to wrongful termination involving medical conditions.
This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. Individual rights vary by circumstance. Consultation with a qualified attorney is strongly recommended.
Employees managing documented medical conditions may face complex challenges in the workplace, particularly when termination follows medical disclosure or a request for accommodations. Under California’s Fair Employment and Housing Act (FEHA) and the federal Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), employees may be protected against adverse employment actions that arise due to qualifying medical conditions.
This article provides informational insight into statutory violation indicators under California law. It does not provide legal advice or assessment tools. Individual legal outcomes depend on context, documentation, and statutory interpretation.
Statutory Obligations Related to Medical Conditions
Under FEHA, employers are prohibited from discriminating against employees with medical conditions that qualify as disabilities. Covered conditions may include, but are not limited to:
- Cancer
- Epilepsy
- HIV/AIDS
- Diabetes
- Autoimmune disorders
- Multiple sclerosis
- Migraines and seizure-related conditions
If a condition substantially limits one or more major life activities—such as walking, working, immune function, or neurological processes—statutory protections may apply.
Statutory obligations may include:
- Reasonable accommodations, unless they impose undue hardship to the employer
- A good-faith interactive process to explore those accommodations
- Prohibition of retaliation related to medical disclosures or accommodation requests
FEHA generally applies to California employers with five or more employees and may provide broader protection than the federal ADA.
Employer Conduct That Might Indicate Statutory Non-Compliance
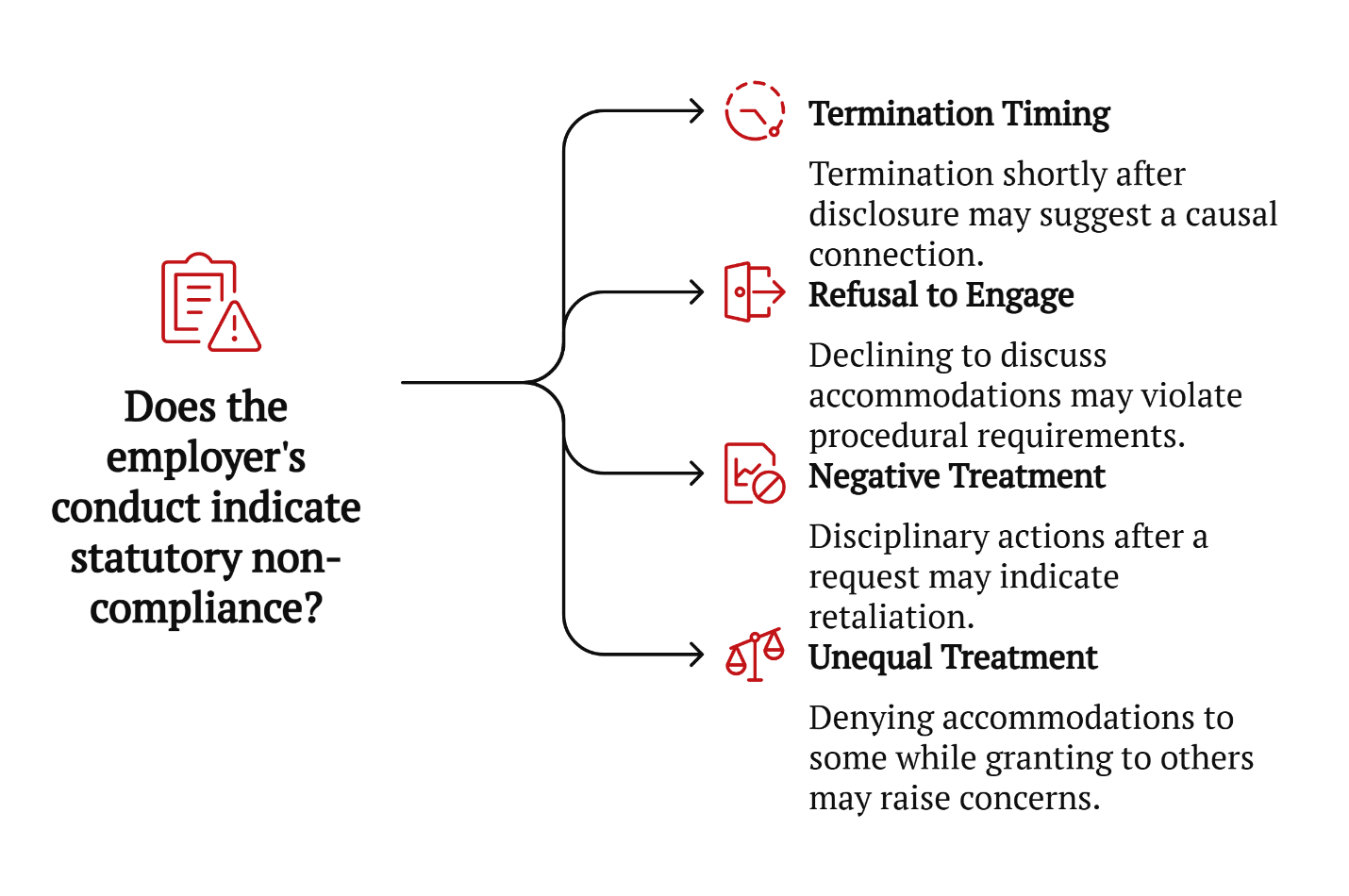
When medical information is shared in good faith, employers are expected to act in accordance with state and federal obligations. Certain behaviors may suggest non-compliance, particularly when accompanied by a lack of documentation or explanation.
Potential red flag patterns include:
- Termination shortly after disclosure of medical condition
An employee is terminated within days or weeks of disclosing a serious medical condition or requesting an accommodation. The timing may suggest a causal connection. - Refusal to engage in the interactive process
Employers who decline to discuss possible accommodations or refuse to acknowledge documentation may not be meeting procedural requirements. - Negative treatment after a request
Disciplinary action, shift reassignment, or performance write-ups issued after a request for accommodation may help establish retaliation concerns. - Unequal treatment
When similarly situated employees without medical conditions receive accommodations or flexibility denied to others, it may raise statutory concerns.
These patterns do not automatically mean a violation has occurred but may indicate the need for legal review.
Illustrative Examples of Potential Violations
Example 1:
An employee undergoing chemotherapy submits a physician’s note requesting a temporary reduction in workload. Within a week, the employer terminates the employee, citing “staffing adjustments” with no documented performance issues.
This timing may raise concerns about retaliatory action and failure to accommodate.
This example is illustrative only and does not constitute legal advice. Similar facts may result in different outcomes depending on specific circumstances.
Example 2:
A warehouse employee with epilepsy requests a shift change to avoid night work that could trigger seizures. The employer rejects the request without exploring alternatives or documenting the basis for denial.
This may indicate failure to engage in the interactive process under FEHA.
Red Flags
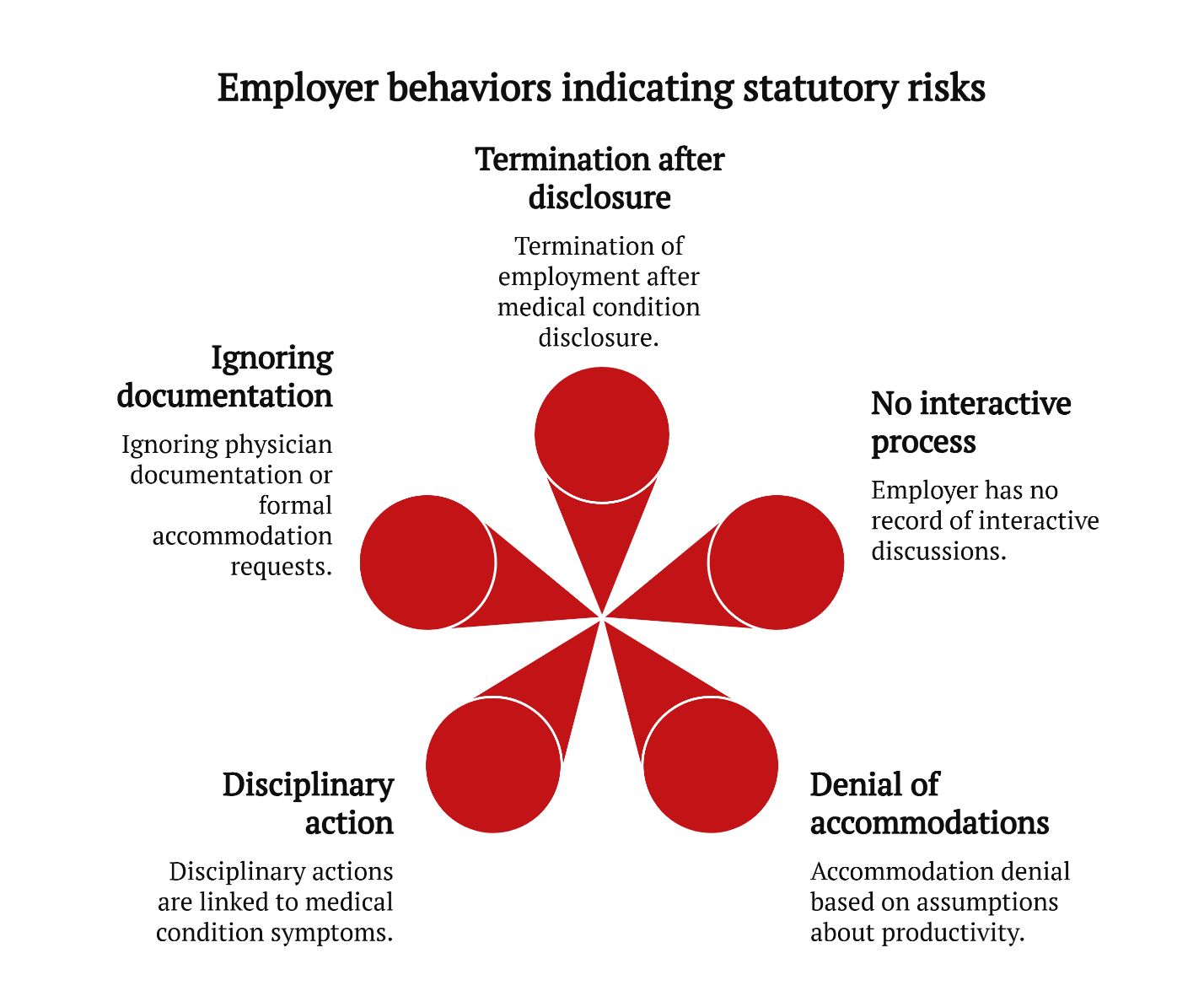
Certain behaviors by employers—including but not limited to the following—may help identify statutory risks:
- Termination following disclosure of a qualifying medical condition
- No record of engagement in the interactive process
- Denial of accommodations based on assumptions about productivity or future absences
- Disciplinary action tied to symptoms of a medical condition
- Ignoring physician documentation or formal accommodation requests
Maintaining documentation such as emails, HR responses, accommodation letters, and performance records may support legal evaluation. Professional legal consultation is essential for documented statutory violations.
Conclusion
Wrongful termination due to medical conditions may involve statutory non-compliance with California FEHA or the ADA. While not all adverse actions are unlawful, certain conduct—particularly when accompanied by documentation—may warrant further examination.
Understanding these patterns is not a substitute for legal analysis.
Consult a qualified California employment attorney if you have experienced termination, denial of accommodations, or disciplinary action following medical disclosures.
FAQs
What employer conduct may indicate a violation under California disability discrimination law?
Conduct such as denying reasonable accommodations, failing to engage in the interactive process, or terminating an employee shortly after a medical disclosure may indicate potential non-compliance with FEHA.
How can medical documentation help support a potential wrongful termination concern?
Documentation—including but not limited to physician notes, written accommodation requests, and HR correspondence—may help establish a timeline and pattern of employer conduct relevant to legal analysis.
FUQs (Frequently Unasked Questions)
Q1: What kinds of medical conditions are typically protected under FEHA?
Conditions such as cancer, epilepsy, autoimmune disorders, HIV/AIDS, and other chronic or serious medical issues may qualify as disabilities if they substantially limit a major life activity.
Q2: Can denial of a work schedule change constitute a statutory violation?
If the request is related to a qualifying medical condition and the employer denies it without engaging in a good-faith interactive process, it may suggest a statutory violation under FEHA or ADA.
Disclaimer:
This content is for informational purposes only. This content is not legal advice. No attorney-client relationship is formed through this content. Please consult a qualified attorney in your jurisdiction for legal advice specific to your situation.
Protect Your Rights | The Akopyan Law Firm, A.P.C. | Top Gun Employment Lawyers
Have you been wrongfully terminated from your job? Have you suffered discrimination, harassment, or retaliation in the workplace? Has your employer violated wage and hour laws? If so, we can help. The Akopyan Law Firm, A.P.C. is dedicated to protecting and enforcing employees’ rights throughout Southern California. With a 97% success rate and millions recovered for our clients, our team of experienced and talented employment lawyers can fight to secure the justice you deserve.
Take the First Step Towards Securing Justice: Call us today to speak with one of our experienced employment lawyers. The firm offers case evaluations free of charge.
Contact Us Today:
- Phone: (818) 509-9975
- Office Locations: Los Angeles, Bakersfield, Costa Mesa, Temecula, Rancho Cucamonga, Oxnard, Culver City, and San Diego in California.
Important: Contacting the Akopyan Law Firm, A.P.C. does not create an attorney-client relationship, but all communications will remain private and confidential. Each case is unique. The Akopyan Law Firm, A.P.C., does not guarantee any outcome.

